Biomechanical basis of human movement 5th edition – The Biomechanical Basis of Human Movement, 5th Edition, embarks on an enlightening journey, delving into the intricate interplay between mechanics and human locomotion. This authoritative text unravels the fundamental principles governing movement, offering a comprehensive understanding of the musculoskeletal system, kinematics, kinetics, and their practical applications.
Through its meticulously crafted chapters, this seminal work elucidates the concepts of force, motion, and energy in the context of human movement. It meticulously examines the structure and function of the musculoskeletal system, highlighting the harmonious interplay of muscles, bones, and joints in orchestrating movement.
Furthermore, it explores the principles of kinematics and kinetics, demonstrating their indispensable role in analyzing and assessing human movement patterns.
Biomechanical Principles
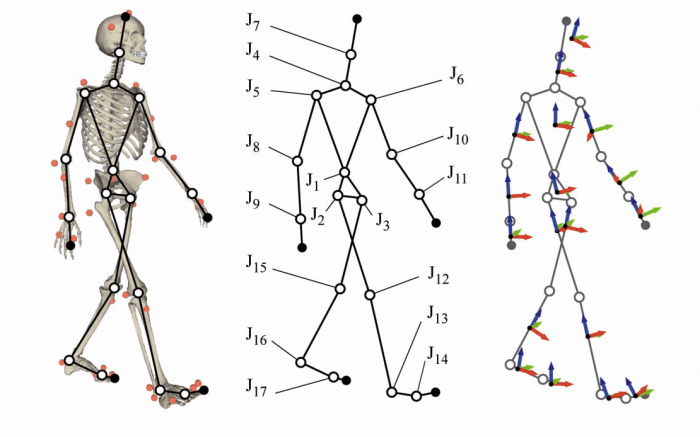
Biomechanics is the study of the mechanical laws relating to the movement of living organisms. When applied to human movement, biomechanics seeks to understand how the body generates, controls, and absorbs forces during movement. This knowledge is essential for understanding normal movement, assessing movement disorders, and designing effective rehabilitation programs.
The fundamental principles of biomechanics that relate to human movement include:
- Force: A force is any interaction that changes the motion of an object. Forces can be applied to the body from external sources (e.g., gravity, friction) or from internal sources (e.g., muscle contractions).
- Motion: Motion is the change in position of an object over time. Motion can be described in terms of displacement, velocity, and acceleration.
- Energy: Energy is the ability to do work. Energy can be transferred between objects in various forms, including mechanical energy (e.g., kinetic energy, potential energy), heat, and sound.
Musculoskeletal System
The musculoskeletal system is composed of the bones, muscles, and joints of the body. These structures work together to produce movement, support the body, and protect the internal organs.
Bonesprovide the rigid framework of the body and serve as levers for muscle action. Musclesare responsible for generating force and producing movement. Jointsconnect the bones and allow for movement between them.
Connective tissue, including tendons, ligaments, and fascia, supports and protects the musculoskeletal system. Tendonsconnect muscles to bones, while ligamentsconnect bones to bones. Fasciais a type of connective tissue that wraps around muscles, bones, and joints, providing support and protection.
Kinematics and Kinetics
Kinematicsis the study of motion without regard to the forces that cause it. Kinematic analysis can be used to describe the movement of body segments, such as the range of motion of a joint or the velocity of a limb.
Kineticsis the study of the forces that cause motion. Kinetic analysis can be used to determine the forces acting on the body during movement, such as the ground reaction force or the muscle forces that produce movement.
Kinematics and kinetics are often used together to analyze human movement. This approach can provide a comprehensive understanding of how the body moves and the forces that are involved.
Gait Analysis
Gait analysis is the study of human walking. Gait analysis can be used to assess normal and abnormal gait patterns, and to design rehabilitation programs for individuals with gait disorders.
The gait cycle is divided into two phases: the stance phaseand the swing phase. The stance phase begins when the heel strikes the ground and ends when the toes push off the ground. The swing phase begins when the toes push off the ground and ends when the heel strikes the ground again.
Gait analysis can be used to assess a variety of gait parameters, including:
- Stride length
- Step length
- Cadence
- Joint angles
- Muscle activity
Ergonomics
Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between humans and their work environment. Ergonomics seeks to design workplaces and products that are safe, comfortable, and efficient for users.
Ergonomic principles can be applied to a variety of settings, including offices, factories, and homes. Ergonomic interventions can help to reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders, such as back pain, neck pain, and carpal tunnel syndrome.
Examples of ergonomic interventions include:
- Adjustable chairs and desks
- Footrests
- Wrist rests
- Proper lighting
Rehabilitation
Biomechanics plays an important role in rehabilitation. Biomechanical principles can be used to design rehabilitation programs for individuals with movement disorders.
Rehabilitation programs that incorporate biomechanical principles can help to improve:
- Range of motion
- Strength
- Balance
- Coordination
- Function
Examples of successful rehabilitation programs that have incorporated biomechanical principles include:
- Programs for individuals with spinal cord injuries
- Programs for individuals with stroke
- Programs for individuals with cerebral palsy
Common Queries: Biomechanical Basis Of Human Movement 5th Edition
What is the significance of biomechanics in understanding human movement?
Biomechanics provides a scientific framework for analyzing the forces, motions, and energy involved in human movement, enabling a deeper understanding of how the body functions during various activities.
How does the musculoskeletal system contribute to movement?
The musculoskeletal system, comprising muscles, bones, and joints, serves as the mechanical apparatus that generates, transmits, and controls movement. Muscles provide the force for movement, while bones provide structural support and leverage, and joints facilitate the articulation of bones.
What is the role of kinematics and kinetics in biomechanics?
Kinematics focuses on describing the motion of objects without considering the forces involved, while kinetics analyzes the forces that cause and influence motion. Together, kinematics and kinetics provide a comprehensive understanding of movement patterns.