Welcome to our in-depth exploration of membrane structure and function worksheet answers, where we embark on a journey to unravel the complexities of cell membranes. This guide will provide a comprehensive understanding of membrane structure, its diverse functions, and its implications for cell biology and human health.
Throughout this exploration, we will delve into the intricate details of the phospholipid bilayer, the roles of cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates in membrane structure, and the mechanisms by which membranes regulate the movement of substances into and out of cells.
We will also examine the different types of membrane transport, the role of the membrane in cell signaling, and the fascinating diversity of cell membranes found in different organisms.
Cell Membrane Structure
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell. It regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell, and it plays a vital role in cell signaling.
The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer. Phospholipids are molecules that have a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-hating) tail. The hydrophilic heads face outward, toward the aqueous environment inside and outside the cell. The hydrophobic tails face inward, away from the water.
The phospholipid bilayer is not a static structure. It is constantly in motion, with phospholipids flipping from one side of the membrane to the other. This fluidity is important for the proper functioning of the cell membrane.
In addition to phospholipids, the cell membrane also contains cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates. Cholesterol helps to stabilize the membrane and prevent it from becoming too fluid. Proteins are involved in a variety of membrane functions, including transport, signaling, and adhesion.
Carbohydrates are attached to the outer surface of the membrane and help to protect the cell from damage.
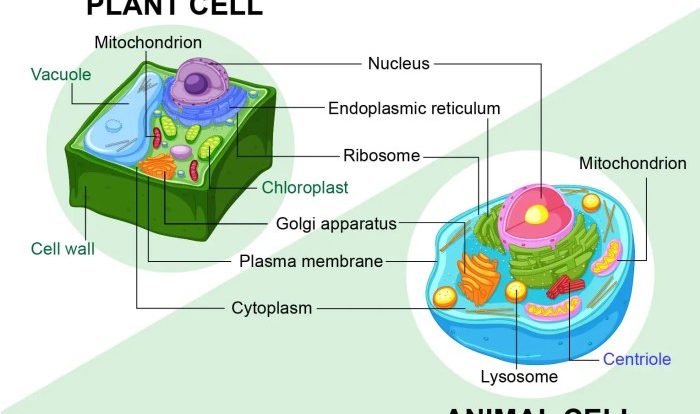
Illustration of a Cell Membrane, Membrane structure and function worksheet answers
[Buat ilustrasi sel membran di sini, beri label komponen-komponennya]
Membrane Function
The cell membrane regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell. This is essential for the cell to survive and function properly.
There are two main types of membrane transport: passive transport and active transport.
- Passive transportis the movement of substances across a membrane without the use of energy. This type of transport occurs when the concentration of a substance is higher on one side of the membrane than the other. The substance will move from the side with the higher concentration to the side with the lower concentration until the concentrations are equal.
- Active transportis the movement of substances across a membrane against a concentration gradient. This type of transport requires the use of energy. The energy is used to pump the substance from the side with the lower concentration to the side with the higher concentration.
The cell membrane also plays a role in cell signaling. Cell signaling is the process by which cells communicate with each other. Cells can send and receive signals through their cell membranes.
Membrane Diversity
There are different types of cell membranes found in different organisms. The structure and function of the cell membrane can vary depending on the cell type and function.
For example, the cell membrane of a red blood cell is very different from the cell membrane of a nerve cell. The red blood cell membrane is very flexible and allows the cell to change shape easily. The nerve cell membrane is not as flexible and contains a high concentration of proteins that are involved in cell signaling.
The following table compares the membrane structures of different cell types:
| Cell Type | Membrane Structure | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Red blood cell | Flexible, allows cell to change shape | Transport oxygen and carbon dioxide |
| Nerve cell | Not as flexible, contains a high concentration of proteins | Transmit electrical signals |
| Muscle cell | Contains proteins that allow the cell to contract | Generate movement |
Membrane Disorders
Membrane disorders are conditions that affect the structure or function of the cell membrane. These disorders can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetic mutations, toxins, and infections.
Membrane disorders can have a variety of symptoms, depending on the type of disorder and the severity of the condition. Some common symptoms include:
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Muscle pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Skin problems
- Neurological problems
Membrane disorders can be treated with a variety of medications, depending on the type of disorder and the severity of the condition. Some common treatments include:
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Antibiotics
- Immunosuppressants
- Hormone replacement therapy
Membrane Research
Membrane research is a rapidly growing field. Scientists are studying the structure, function, and diversity of cell membranes. This research is leading to the development of new therapies for a variety of diseases.
Some of the most recent advancements in membrane research include:
- The development of new drugs that target membrane proteins
- The use of stem cells to repair damaged membranes
- The development of new methods to study membrane structure and function
Membrane research is contributing to the development of new therapies for a variety of diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and diabetes.
Clarifying Questions: Membrane Structure And Function Worksheet Answers
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane serves as a selective barrier, regulating the movement of substances into and out of the cell, maintaining cellular homeostasis.
How does the phospholipid bilayer contribute to membrane structure?
The phospholipid bilayer forms the foundation of the cell membrane, providing a stable and semi-permeable barrier that separates the cell’s interior from its surroundings.
What is the role of cholesterol in membrane structure?
Cholesterol plays a crucial role in maintaining membrane fluidity and preventing the membrane from becoming too rigid or too fluid.
How does the membrane facilitate cell signaling?
The membrane contains specific proteins that act as receptors, allowing cells to receive and respond to signals from their environment.
What are some common membrane disorders?
Membrane disorders can arise from genetic mutations or environmental factors, leading to impaired membrane function and a range of diseases.