Embark on an enthralling journey into the depths of Earth’s past with the Age of Rock and Plate Tectonics Quiz. This quiz delves into the captivating world of geology, where rocks hold the key to unlocking the secrets of our planet’s dynamic history.
From the enigmatic formation of rock layers to the colossal forces of plate tectonics, this quiz will guide you through the fundamental principles that shape our understanding of Earth’s evolution.
Age of Rock and Plate Tectonics: Age Of Rock And Plate Tectonics Quiz
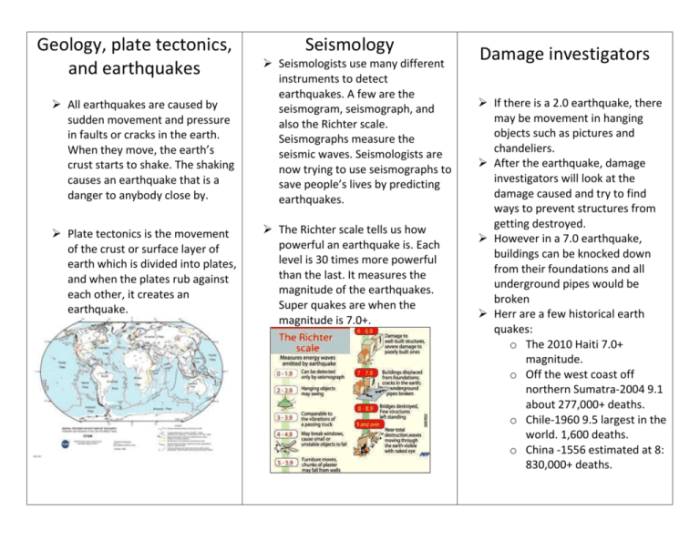
The age of rock is a crucial concept in understanding plate tectonics, as it provides valuable insights into the formation, movement, and evolution of the Earth’s crust. By determining the age of rocks, geologists can reconstruct the sequence of geological events and gain a deeper understanding of the dynamic processes that have shaped our planet.
Methods of Determining the Age of RocksSeveral methods are employed to determine the age of rocks, each with its advantages and limitations. These include:
- Radiometric Dating:This technique measures the decay of radioactive isotopes within rocks to calculate their age. It is highly accurate and widely used for rocks older than a few million years.
- Paleomagnetism:This method analyzes the magnetic orientation of rocks to determine their age based on the Earth’s magnetic field reversals, which occur at regular intervals.
- Biostratigraphy:This approach uses the presence and sequence of fossils in rocks to determine their relative age. It is particularly useful for sedimentary rocks.
- Cross-Cutting Relationships:This method determines the relative age of rocks based on their cross-cutting relationships. A younger rock that cuts across an older rock must have formed after the older rock.
Examples of Age of Rock Supporting Plate Tectonics
The age of rock has played a significant role in supporting the theory of plate tectonics. For instance:
- Seafloor Spreading:The age of rocks on the ocean floor increases away from mid-ocean ridges, providing evidence for the spreading of the seafloor and the creation of new crust.
- Subduction Zones:The age of rocks in subduction zones decreases towards the trench, indicating that younger rocks are being subducted beneath older rocks.
- Mountain Building:The age of rocks in mountain belts often shows a pattern of increasing age from the center outwards, suggesting that the mountains were formed by the collision of tectonic plates.
Rock Layers and Plate Boundaries
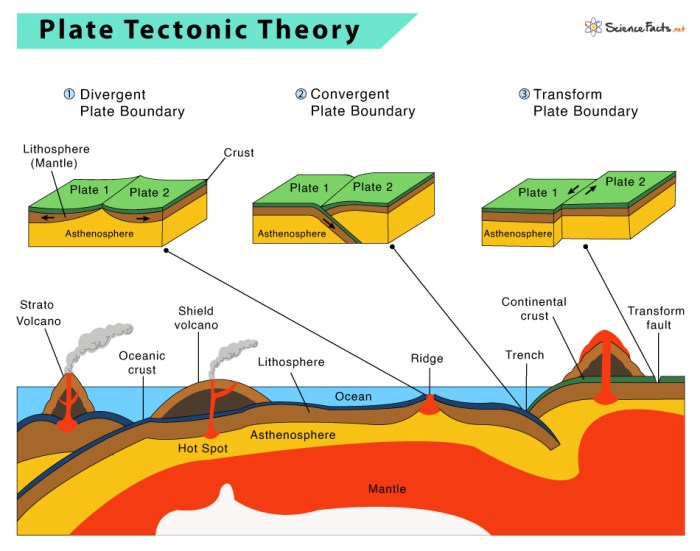
Rock layers provide valuable insights into the movement of tectonic plates over geological time. The relationship between rock layers and plate boundaries is closely intertwined, as the formation and deformation of rock layers are influenced by plate tectonic processes.
Relative Age of Rock Layers
The principle of superposition states that in an undisturbed sequence of sedimentary rocks, the oldest layers are at the bottom and the youngest layers are at the top. This principle allows geologists to determine the relative age of rock layers, which is crucial for understanding the geological history of an area.
Correlation of Rock Layers
Rock layers can be correlated across different locations to establish a regional or global stratigraphic framework. By comparing the lithology, fossil content, and other characteristics of rock layers, geologists can identify and match layers that were formed at the same time, even if they are now separated by great distances.
Tectonic Plate Movements
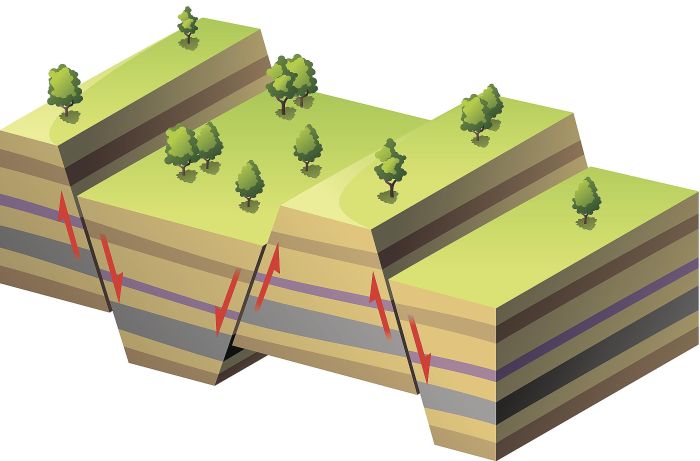
The movement of tectonic plates can cause rock layers to be deformed, folded, faulted, and uplifted. By studying the patterns and orientations of these deformations, geologists can infer the direction and magnitude of past plate movements. For example, folded and thrust-faulted rock layers indicate compressional forces associated with plate collisions, while normal faults and rift basins indicate extensional forces associated with plate divergence.
Examples of Plate Reconstruction
The use of rock layers has played a significant role in reconstructing past plate movements. For instance, the identification of similar rock sequences on different continents led to the development of the theory of continental drift, which proposed that the continents were once joined together in a supercontinent called Pangea.
Another example is the use of magnetic stripes on the ocean floor to reconstruct the history of seafloor spreading. By measuring the age of the magnetic stripes, geologists have been able to determine the rate and direction of plate movements over time.
Plate Tectonics and Rock Deformation
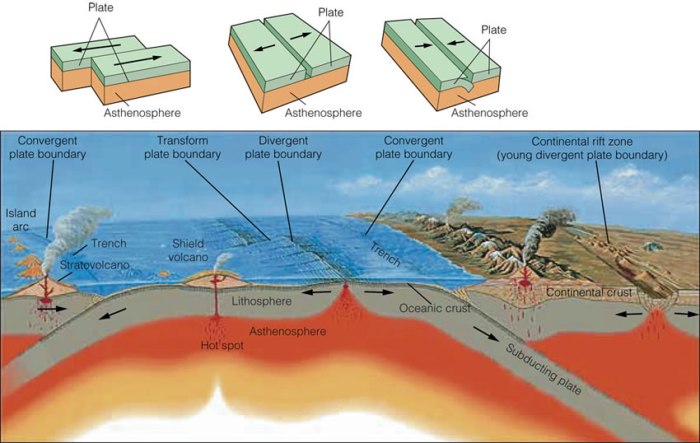
Plate tectonics plays a significant role in rock deformation. When tectonic plates move, they can collide, separate, or slide past each other. These interactions can cause rocks to fold, fault, or metamorphose.
The age of rock can be used to determine the timing of tectonic events. For example, if a layer of rock is found to be younger than a layer of rock that has been folded, then the folding must have occurred after the younger layer was deposited.
Examples of Rock Deformation Used to Study Plate Tectonics
- The Appalachian Mountains in North America were formed when the North American and African plates collided.
- The San Andreas Fault in California is a strike-slip fault that is caused by the movement of the Pacific and North American plates.
- The Himalayas in Asia were formed when the Indian and Eurasian plates collided.
Applications of Age of Rock and Plate Tectonics
The study of the age of rock and plate tectonics has made significant contributions to our understanding of Earth’s history and various fields. The principles and knowledge gained from these studies have been applied in numerous practical applications, providing valuable insights into Earth’s geological processes and their implications.
Understanding Earth’s History
The age of rock and plate tectonics provides a chronological framework for understanding Earth’s geological history. By determining the age of rock layers and analyzing their sequences, scientists can reconstruct past geological events, such as mountain building, volcanic eruptions, and climate changes.
This information helps unravel the evolution of Earth’s landscapes, ecosystems, and the processes that have shaped our planet over billions of years.
Natural Resource Exploration, Age of rock and plate tectonics quiz
The principles of age of rock and plate tectonics are essential in the exploration and extraction of natural resources. By understanding the geological formations and structures associated with different types of mineral deposits, geologists can target areas with higher potential for resource discovery.
This knowledge guides exploration efforts, reduces uncertainties, and optimizes resource extraction.
Hazard Mitigation
The study of age of rock and plate tectonics plays a crucial role in hazard mitigation and disaster preparedness. By identifying areas prone to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or landslides, scientists can develop early warning systems, implement building codes, and establish evacuation plans.
This information helps communities prepare for and mitigate the risks associated with geological hazards, reducing the potential for loss of life and property.
Climate Change Studies
The age of rock and plate tectonics provides valuable insights into past climate changes. By analyzing the composition and age of sedimentary rocks, scientists can reconstruct ancient climates and study the factors that have influenced climate variability over geological timescales.
This knowledge helps scientists understand the potential impacts of current climate change and develop strategies for mitigation and adaptation.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the significance of rock age in understanding plate tectonics?
The age of rocks provides crucial evidence for the movement and interactions of tectonic plates, helping geologists reconstruct past plate boundaries and track the evolution of Earth’s surface.
How do rock layers relate to plate boundaries?
Rock layers can be used to infer the location and movement of plate boundaries over time. The age and composition of rock layers can indicate whether they formed at divergent, convergent, or transform boundaries.
What role does plate tectonics play in rock deformation?
Plate tectonics drives rock deformation through processes such as folding, faulting, and metamorphism. The age of deformed rocks can provide insights into the timing and intensity of tectonic events.