Qualitative energy storage & conservation with bar graphs – Qualitative energy storage and conservation with bar graphs provide a powerful means of understanding and optimizing energy usage. This approach offers insights into different energy storage methods, effective conservation techniques, and the role of bar graphs in visualizing energy data.
By exploring these concepts, we uncover strategies for reducing energy consumption, promoting sustainability, and ensuring a more efficient energy future.
This comprehensive guide delves into the advantages and disadvantages of various energy storage technologies, examining their practical applications. It also identifies the most effective energy conservation techniques, showcasing their implementation in different settings. Furthermore, the use of bar graphs to illustrate energy storage capacity, compare energy consumption patterns, and track progress towards conservation goals is thoroughly explained.
Qualitative Energy Storage Methods
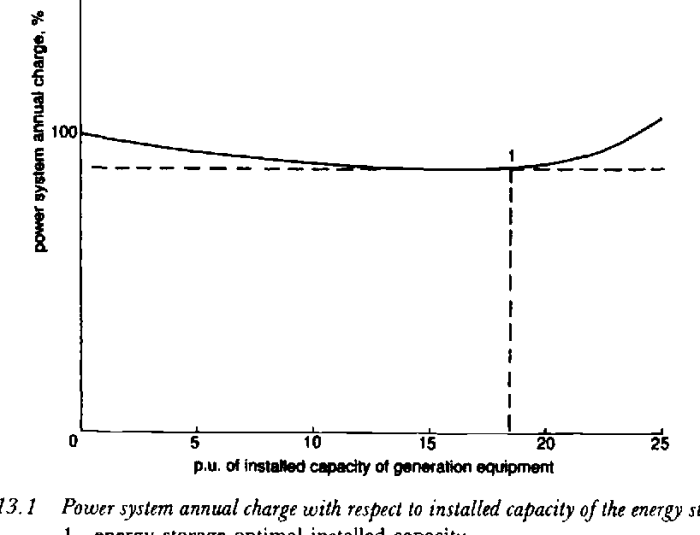
Qualitative energy storage methods refer to the storage of energy in forms other than electricity. These methods offer advantages such as high energy density, long-term storage, and grid independence. However, they also come with drawbacks, including cost, efficiency losses, and environmental concerns.
The most common qualitative energy storage methods include:
- Pumped-storage hydroelectricity: Stores energy by pumping water to a higher elevation during off-peak hours and releasing it to generate electricity during peak hours.
- Flywheels: Store energy as kinetic energy in a spinning rotor, which can be released to generate electricity when needed.
- Compressed air energy storage: Stores energy by compressing air in an underground reservoir, which can be released to drive a turbine and generate electricity.
- Thermal energy storage: Stores energy as heat in a thermal medium, such as molten salt or water, which can be used to generate electricity or provide heat for buildings.
Energy Conservation Techniques
Energy conservation techniques aim to reduce energy consumption without compromising comfort or productivity. Effective techniques include:
- Improving insulation: Reducing heat loss through walls, ceilings, and floors.
- Upgrading windows: Installing energy-efficient windows that reduce heat transfer.
- Using energy-efficient appliances: Choosing appliances with high energy efficiency ratings.
- Optimizing lighting: Using natural light, LED bulbs, and motion sensors to reduce lighting energy consumption.
- Implementing smart energy management systems: Installing devices that monitor and control energy usage.
Bar Graphs for Data Visualization
Bar graphs are a useful tool for visualizing qualitative energy storage capacity and energy consumption data.
To illustrate qualitative energy storage capacity, a bar graph can be created with different technologies on the x-axis and their respective storage capacities on the y-axis. This graph provides a clear comparison of the storage potential of each technology.
To compare energy consumption of different sectors, a bar graph can be created with sectors on the x-axis and their energy consumption on the y-axis. This graph highlights the relative energy usage of different sectors, enabling targeted energy conservation efforts.
Bar graphs can also be used to track progress towards energy conservation goals. By comparing data over time, it is possible to identify areas where energy consumption has been reduced and areas where further improvements can be made.
Case Studies of Qualitative Energy Storage and Conservation: Qualitative Energy Storage & Conservation With Bar Graphs
Numerous projects have successfully implemented qualitative energy storage and conservation measures.
One notable case study is the Bath County Pumped-Storage Station in Virginia, USA. This project uses pumped-storage hydroelectricity to store energy during off-peak hours and generate electricity during peak hours, providing grid stability and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Another example is the Passive House in Darmstadt, Germany. This building is designed to be highly energy-efficient, using passive design principles, triple-glazed windows, and a geothermal heat pump to minimize energy consumption.
These projects demonstrate the potential of qualitative energy storage and conservation measures to reduce energy consumption, improve grid reliability, and mitigate environmental impacts.
Detailed FAQs
What are the advantages of using bar graphs for energy data visualization?
Bar graphs provide a clear and concise visual representation of energy data, making it easy to compare different technologies, sectors, or time periods. They are particularly useful for tracking progress towards energy conservation goals.
How can qualitative energy storage methods contribute to energy conservation?
Qualitative energy storage methods, such as pumped hydro storage and flywheels, can store energy during periods of low demand and release it during periods of high demand, reducing the need for fossil fuel-based generation.
What are some of the most effective energy conservation techniques?
Effective energy conservation techniques include energy-efficient appliances, building insulation, and behavioral changes, such as turning off lights when leaving a room. Implementing these techniques can significantly reduce energy consumption in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.