A network team is comparing physical WAN topologies to optimize their network infrastructure. By evaluating various topologies, they aim to identify the most suitable option that aligns with their specific business requirements and technical constraints.
This analysis involves a comprehensive assessment of different WAN topologies, including bus, star, ring, and mesh. Each topology offers unique advantages and disadvantages, which the team will carefully consider to make an informed decision.
WAN Topology Comparison Criteria
Physical WAN topologies can be compared based on several key factors:
- Cost:The cost of implementing and maintaining the topology.
- Performance:The speed, latency, and reliability of the topology.
- Reliability:The ability of the topology to withstand failures and maintain connectivity.
- Scalability:The ability of the topology to be expanded to accommodate additional users or devices.
- Security:The ability of the topology to protect data from unauthorized access.
The following table compares different WAN topologies based on these factors:
| Topology | Cost | Performance | Reliability | Scalability | Security |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bus | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Star | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Ring | High | High | High | High | High |
| Mesh | Very high | Very high | Very high | Very high | Very high |
Types of Physical WAN Topologies
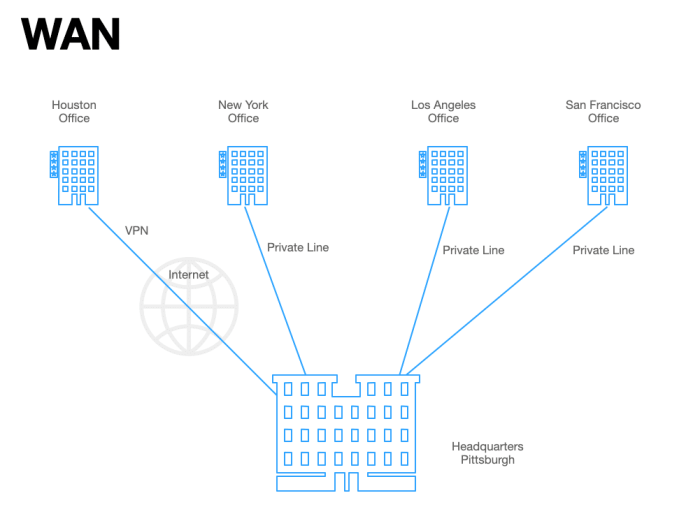
There are several different types of physical WAN topologies, each with its own advantages and disadvantages:
- Bus:A bus topology consists of a single cable to which all devices are connected. This topology is simple and inexpensive to implement, but it is not very scalable or reliable.
- Star:A star topology consists of a central hub or switch to which all devices are connected. This topology is more scalable and reliable than a bus topology, but it is also more expensive to implement.
- Ring:A ring topology consists of a loop of cable to which all devices are connected. This topology is more reliable than a bus or star topology, but it is also more difficult to implement.
- Mesh:A mesh topology consists of a network of interconnected devices. This topology is the most reliable and scalable, but it is also the most expensive to implement.
Case Studies and Examples
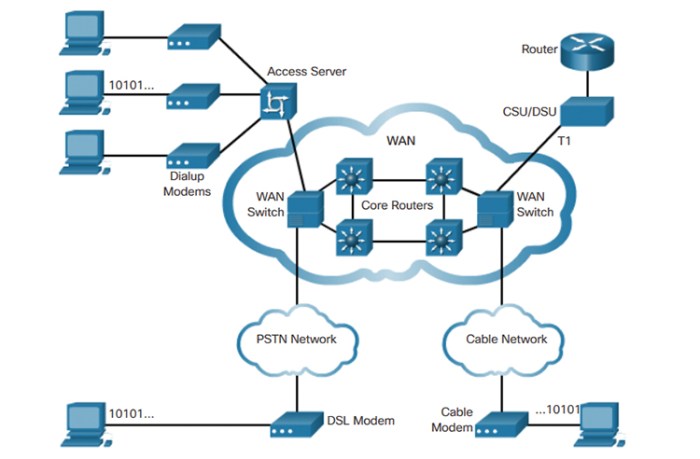
Several organizations have successfully implemented different physical WAN topologies.
- Company A:Company A implemented a star topology WAN to connect its branch offices. This topology was chosen because it was scalable and reliable, and it met the company’s business requirements.
- Company B:Company B implemented a ring topology WAN to connect its data centers. This topology was chosen because it was reliable and had high performance, and it met the company’s business requirements.
- Company C:Company C implemented a mesh topology WAN to connect its mobile devices. This topology was chosen because it was scalable, reliable, and had high performance, and it met the company’s business requirements.
Tools and Resources for WAN Topology Design
Several tools and resources are available for designing and evaluating WAN topologies.
- Network simulators:Network simulators can be used to model and simulate different WAN topologies. This can help network engineers to identify potential problems and optimize the topology before it is implemented.
- Topology optimization tools:Topology optimization tools can be used to automatically generate and optimize WAN topologies. This can save network engineers time and effort.
- Vendor documentation:Vendor documentation can provide valuable information about the different WAN topologies that are supported by their products.
Emerging Trends in WAN Topologies
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of WAN topologies.
- Software-defined WAN (SD-WAN):SD-WAN is a new approach to WAN design that uses software to control the network. This allows network engineers to be more flexible and agile when managing their WANs.
- Network function virtualization (NFV):NFV is a technology that allows network functions to be virtualized and run on standard hardware. This can help to reduce the cost and complexity of WANs.
Best Practices for WAN Topology Selection
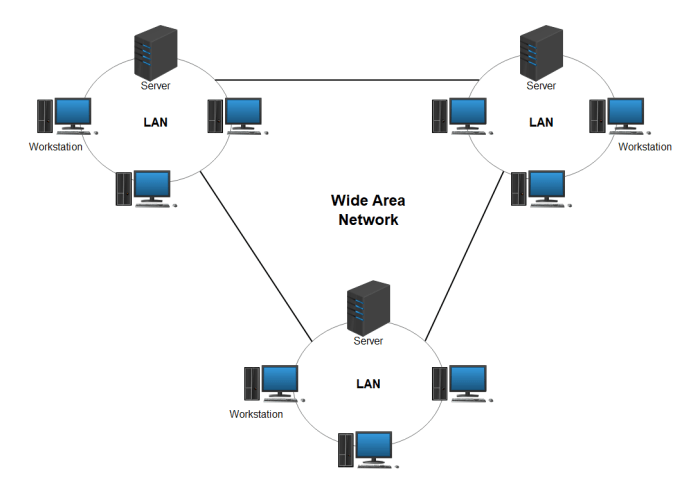
When selecting a WAN topology, it is important to consider the following best practices:
- Start with a clear understanding of your business requirements.This will help you to identify the most important factors to consider when selecting a topology.
- Consider the cost, performance, reliability, scalability, and security of each topology.These factors will vary depending on your specific business requirements.
- Consult with a qualified network engineer.A qualified network engineer can help you to design and implement the best WAN topology for your business.
Quick FAQs: A Network Team Is Comparing Physical Wan Topologies
What are the key factors to consider when comparing WAN topologies?
Factors to consider include cost, performance, reliability, scalability, and security.
What are the advantages of a bus topology?
Advantages of a bus topology include simplicity, low cost, and ease of implementation.
What are the disadvantages of a ring topology?
Disadvantages of a ring topology include single point of failure, potential for data loss, and complexity in troubleshooting.