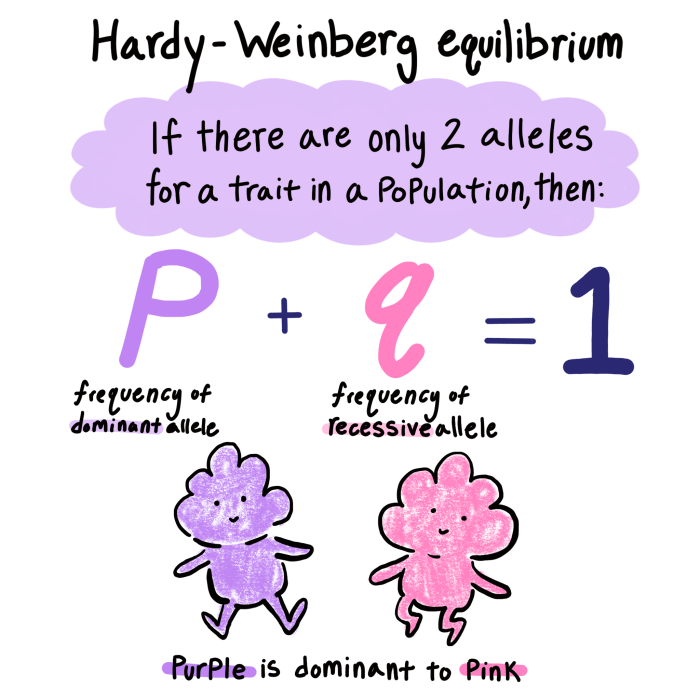The hardy weinberg equation pogil answers – The Hardy-Weinberg equation, a cornerstone of population genetics, offers a profound understanding of allele and genotype frequencies within populations. This equation, named after Godfrey Harold Hardy and Wilhelm Weinberg, serves as a fundamental tool for unraveling the genetic makeup of populations and predicting their evolutionary trajectories.
The Hardy-Weinberg equation assumes an idealized population in equilibrium, where evolutionary forces such as mutation, migration, and selection are absent. Within such populations, allele and genotype frequencies remain constant across generations. However, deviations from this equilibrium can occur due to various factors, providing insights into the evolutionary dynamics of real-world populations.
Hardy-Weinberg Equation: The Hardy Weinberg Equation Pogil Answers
The Hardy-Weinberg equation is a mathematical model that describes the allele and genotype frequencies in a population that is not evolving. It is based on the assumption that there is no selection, no mutation, no migration, no non-random mating, and the population is large.
The equation is:
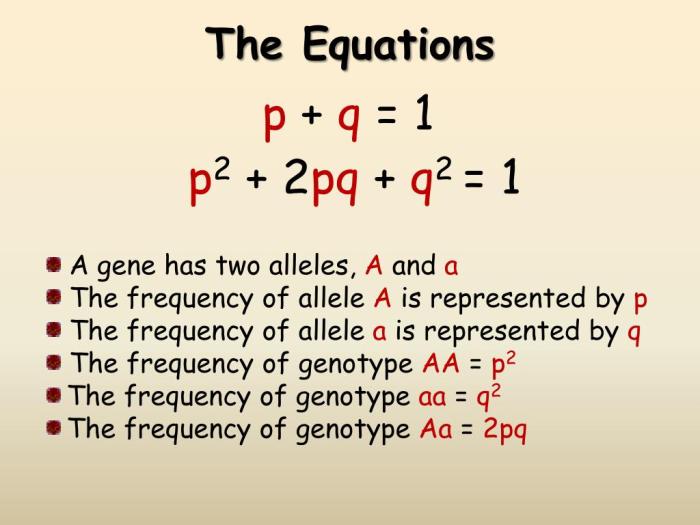
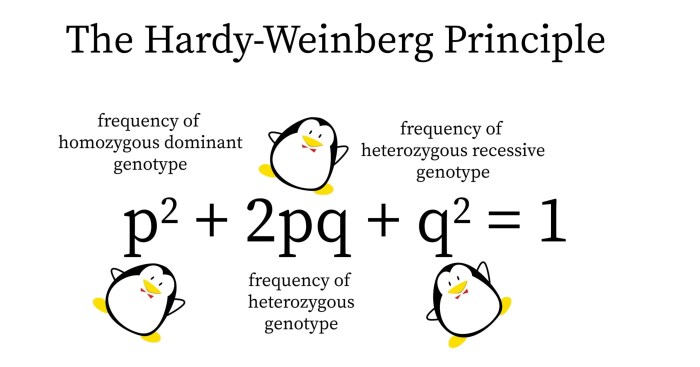
p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1
where p is the frequency of the dominant allele, q is the frequency of the recessive allele, p^2 is the frequency of the homozygous dominant genotype, q^2 is the frequency of the homozygous recessive genotype, and 2pq is the frequency of the heterozygous genotype.
The Hardy-Weinberg equation is important because it provides a baseline against which to compare real populations. If a population is not in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, then it is evolving.
Population Genetics, The hardy weinberg equation pogil answers
Population genetics is the study of the allele and genotype frequencies in populations. It is a branch of genetics that is concerned with the genetic variation within and between populations.
The Hardy-Weinberg equation is a fundamental principle of population genetics. It can be used to predict the allele and genotype frequencies in a population that is not evolving.
The factors that can affect the allele and genotype frequencies in a population include:
- Mutation
- Selection
- Migration
- Non-random mating
- Genetic drift
Applications of the Hardy-Weinberg Equation
The Hardy-Weinberg equation is used in a variety of population studies. It can be used to:
- Predict the allele and genotype frequencies in a population that is not evolving
- Estimate the mutation rate
- Identify the factors that are affecting the evolution of a population
- Test for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
Deviations from Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
There are a number of conditions that can lead to deviations from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. These include:
- Selection
- Mutation
- Migration
- Non-random mating
- Genetic drift
Deviations from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium can be used to identify the factors that are affecting the evolution of a population.
Case Study: Human Population Genetics
The Hardy-Weinberg equation has been used to study the allele and genotype frequencies in human populations. This has helped to identify the factors that are affecting the evolution of human populations.
For example, the Hardy-Weinberg equation has been used to study the allele and genotype frequencies of the sickle cell allele in human populations. This has helped to identify the factors that are affecting the evolution of the sickle cell allele in human populations.
The sickle cell allele is a recessive allele that causes sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia is a serious disease that can lead to death. The sickle cell allele is more common in African populations than in other populations. This is because the sickle cell allele provides protection against malaria.
Malaria is a serious disease that is transmitted by mosquitoes. The sickle cell allele provides protection against malaria because it causes the red blood cells to become sickle-shaped. This makes it difficult for the malaria parasite to infect the red blood cells.
The Hardy-Weinberg equation has helped to identify the factors that are affecting the evolution of the sickle cell allele in human populations. This has helped to develop new treatments for sickle cell anemia.
Q&A
What is the significance of the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
The Hardy-Weinberg equation provides a baseline for understanding allele and genotype frequencies in populations. It allows researchers to determine whether a population is in equilibrium and identify factors that may be causing deviations from equilibrium.
What are the assumptions of the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
The Hardy-Weinberg equation assumes random mating, no mutation, no migration, no genetic drift, and no selection. These assumptions create an idealized population that serves as a reference point for understanding real-world populations.
How can the Hardy-Weinberg equation be used in practice?
The Hardy-Weinberg equation can be used to predict allele and genotype frequencies in future generations, estimate the frequency of recessive alleles in a population, and identify populations that are not in equilibrium. It also finds applications in conservation genetics, medicine, and forensic science.