The primary master PATA hard disk, a cornerstone of computer systems, plays a pivotal role in data storage and retrieval. Its unique characteristics and applications make it an essential component for various computing needs. Let’s delve into the world of PATA hard disks, exploring their technical specifications, installation processes, data management techniques, and diverse use cases.
PATA hard disks, also known as Parallel ATA or IDE hard disks, have been widely used in personal computers and other electronic devices. They connect to the motherboard using a parallel interface, allowing for data transfer between the storage device and the system’s memory.
While SATA (Serial ATA) interfaces have become more prevalent in recent years, PATA hard disks remain a reliable and cost-effective option for many applications.
Primary Master PATA Hard Disk
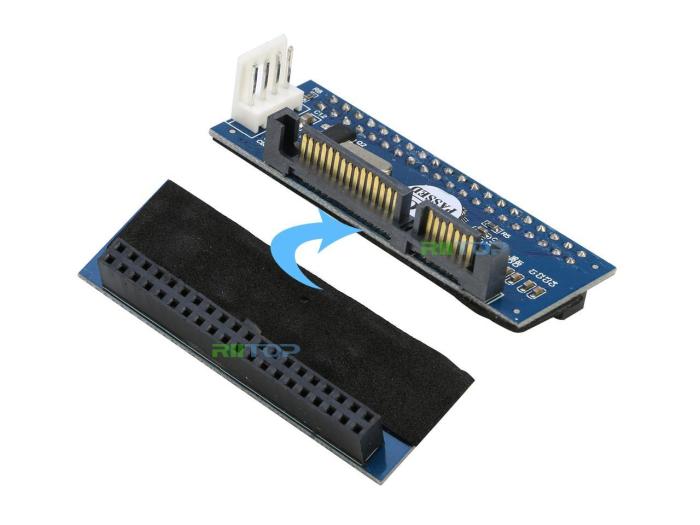

In a computer system, storage devices play a crucial role in storing and retrieving data. Among various storage devices, the primary master PATA hard disk holds a significant position. PATA, short for Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment, is an interface standard used to connect storage devices to the motherboard.
The primary master PATA hard disk is the first and primary storage device in a PATA-based system.
Role of a PATA Hard Disk
The primary master PATA hard disk serves as the main storage unit in a computer system. It is responsible for storing the operating system, applications, and user data. The hard disk is divided into sectors and tracks, which are organized in a specific manner to facilitate efficient data storage and retrieval.
When the computer boots up, the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) accesses the primary master PATA hard disk to load the operating system into memory.
Advantages of Using a PATA Hard Disk
- Cost-effective:PATA hard disks are generally more affordable compared to other storage devices like solid-state drives (SSDs).
- Wide compatibility:PATA hard disks are compatible with a wide range of motherboards and operating systems, making them a versatile storage option.
- Large storage capacity:PATA hard disks offer ample storage capacity, making them suitable for storing large amounts of data.
Disadvantages of Using a PATA Hard Disk
- Limited speed:PATA hard disks have a slower data transfer rate compared to newer storage technologies like SATA (Serial ATA) and NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express).
- Higher latency:PATA hard disks have higher latency than other storage devices, which can impact the overall performance of the system.
- Outdated technology:PATA is an older technology that has been replaced by more advanced storage interfaces, making it less prevalent in modern computer systems.
Technical Specifications
A typical primary master PATA hard disk features specific technical specifications that determine its performance and functionality. These specifications include:
Storage Capacity
- Measured in gigabytes (GB) or terabytes (TB), storage capacity refers to the amount of data the hard disk can hold.
- PATA hard disks typically have capacities ranging from a few GB to hundreds of GB.
Interface
- PATA, also known as Parallel ATA (Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment), is a legacy interface used to connect storage devices to the computer’s motherboard.
- PATA uses a parallel data transfer method, where data is transmitted on multiple wires simultaneously.
Data Transfer Rate
- Measured in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps), data transfer rate indicates the speed at which data can be read from or written to the hard disk.
- PATA hard disks typically have data transfer rates ranging from 133 Mbps to 1000 Mbps (1 Gbps).
Form Factor
- Form factor refers to the physical size and shape of the hard disk.
- PATA hard disks commonly use the 3.5-inch form factor, designed for desktop computers.
Key Differences Between PATA and Other Hard Disk Interfaces
PATA differs from other hard disk interfaces, such as SATA (Serial ATA) and NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express), in several key ways:
- Data Transfer Method:PATA uses a parallel data transfer method, while SATA and NVMe use serial data transfer methods.
- Connector Type:PATA hard disks use a 40-pin IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) connector, while SATA hard disks use a 7-pin SATA connector and NVMe hard disks use a PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) connector.
- Data Transfer Rate:PATA hard disks have lower data transfer rates compared to SATA and NVMe hard disks.
Factors Affecting PATA Hard Disk Performance
Several factors can influence the performance of a PATA hard disk:
- Storage Capacity:Larger storage capacity hard disks tend to have higher performance due to increased data storage space.
- Data Transfer Rate:Hard disks with higher data transfer rates can read and write data faster, improving overall performance.
- Cache Size:A larger cache size allows the hard disk to store frequently accessed data, reducing access time and improving performance.
- Fragmentation:Data fragmentation can slow down hard disk performance by increasing the time it takes to locate and access data.
Installation and Configuration
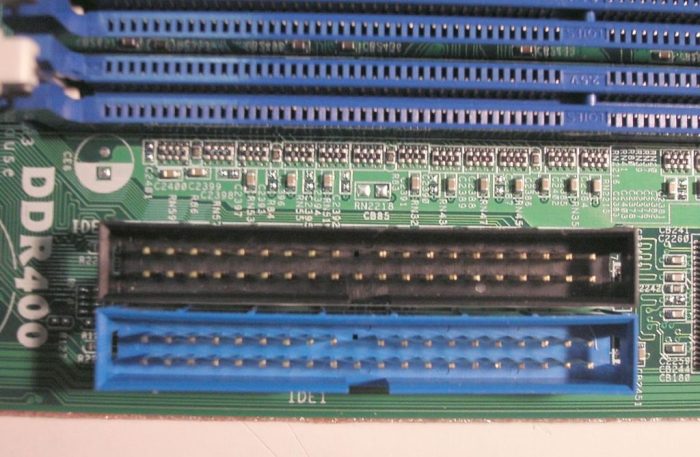
Installing and configuring a primary master PATA hard disk involves several steps. Firstly, physically install the hard disk by connecting it to the motherboard using a PATA cable and power supply. Ensure the cable is securely fastened to both the hard disk and the motherboard.Next,
configure the BIOS settings to recognize the hard disk. Enter the BIOS setup utility, typically by pressing a specific key during system startup (e.g., Del, F2, or F10). Locate the section for storage devices and set the primary master PATA hard disk as the first boot device.
Additionally, enable the hard disk controller and configure the appropriate transfer mode (e.g., PIO or DMA).After configuring the BIOS settings, save the changes and restart the system. The operating system should now detect and initialize the hard disk. Format the hard disk and partition it as desired.
Finally, install the operating system and any necessary drivers.
Troubleshooting Common Installation and Configuration Issues
If you encounter issues during installation or configuration, check the following:
- Ensure the hard disk is properly connected to the motherboard and power supply.
- Verify the BIOS settings are correct, particularly the boot order and hard disk controller settings.
- Check the hard disk for any physical damage or loose connections.
- Update the BIOS to the latest version if necessary.
- Try using a different PATA cable or power supply to eliminate potential hardware issues.
Data Management: Primary Master Pata Hard Disk

Managing data effectively is crucial for optimizing the performance and reliability of a primary master PATA hard disk. This involves implementing strategies for data organization, backup, and retrieval.
Data Organization
Organizing data efficiently allows for faster access and retrieval. One common approach is to categorize data into folders and subfolders based on file type, project, or any other relevant criteria. Additionally, using descriptive file names and avoiding duplicate files can further enhance data management.
For those who are into tech, the primary master PATA hard disk is a crucial component in your computer system. Its primary function is to store and retrieve data, acting as the backbone of your computer’s memory. If you’re looking for a unique perspective on technology, check out the skunk by seamus heaney for a thought-provoking literary exploration of the interplay between technology and nature.
Returning to the primary master PATA hard disk, its efficient data management ensures seamless operation of your computer, making it an indispensable part of your tech setup.
Data Backup and Recovery
Regular data backups are essential to protect against data loss due to hardware failure, accidental deletion, or other unforeseen events. There are various backup methods available, including local backups to external storage devices and cloud-based backup services. Establishing a robust backup plan and regularly testing the recovery process ensures that data can be restored quickly and reliably.
Data Storage and Retrieval Optimization
Optimizing data storage and retrieval involves implementing techniques to reduce data fragmentation and improve access speeds. Defragmentation tools can be used to consolidate fragmented files, while caching mechanisms can speed up access to frequently used data. Additionally, using appropriate file systems and data compression techniques can further enhance storage efficiency and retrieval performance.
Applications and Use Cases

Primary master PATA hard disks have found widespread use in various applications due to their reliability, compatibility, and affordability. They are particularly suitable for scenarios that require large storage capacities and fast data access.
Suitability for Different Workloads
PATA hard disks are well-suited for workloads that involve sequential read/write operations, such as:
- File storage and retrieval
- Database management
- Multimedia applications (e.g., video editing, audio recording)
- Operating system and application storage
However, they may not be ideal for workloads that require high levels of random access, such as:
- Real-time data processing
- Online transaction processing
- Virtualization
Real-World Examples, Primary master pata hard disk
Here are some real-world scenarios where PATA hard disks are commonly used:
- Desktop and laptop computers for general-purpose computing
- File servers for storing and sharing data
- Backup and recovery systems
- Media centers for storing and playing multimedia content
- Embedded systems (e.g., industrial controllers, medical devices)
FAQ Insights
What is the difference between PATA and SATA hard disks?
PATA (Parallel ATA) and SATA (Serial ATA) are two different interfaces used to connect hard disks to a computer’s motherboard. PATA uses a parallel interface, while SATA uses a serial interface. SATA is generally faster and more efficient than PATA, and it has become the standard interface for connecting hard disks in modern computers.
How do I install a primary master PATA hard disk?
Installing a primary master PATA hard disk is a relatively simple process. First, you need to physically connect the hard disk to the motherboard using a PATA cable. Then, you need to configure the BIOS settings to recognize the hard disk.
Once the hard disk is recognized by the BIOS, you can format it and install an operating system.
What are the advantages of using a PATA hard disk?
PATA hard disks are relatively inexpensive and easy to install. They are also compatible with a wide range of motherboards. However, PATA hard disks are not as fast as SATA hard disks, and they have a lower data transfer rate.